|
Page 2 of 3

Distortion
The lens shows a moderate amount of barrel distortion. This can be visible in critical shots especially with straight lines near the image borders. However, the distortion is uniform and easy to correct in post processing.
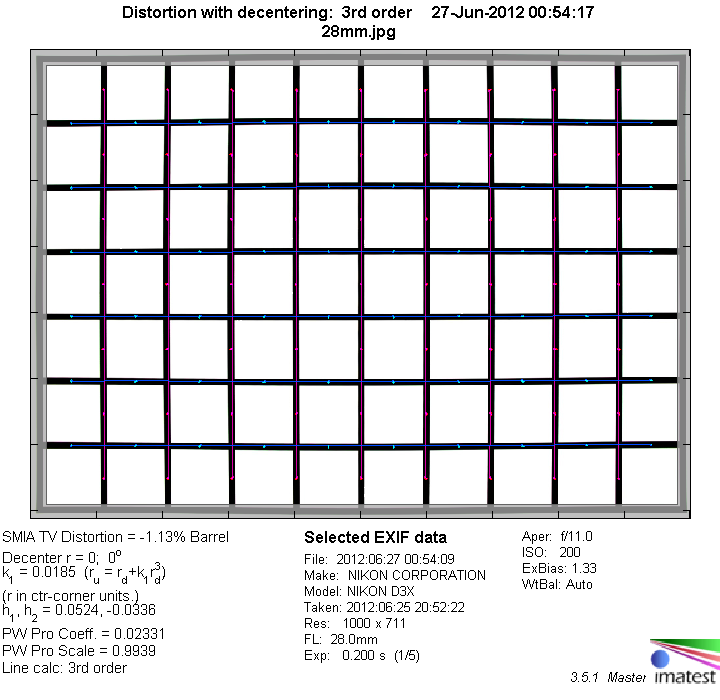
The chart above has a real-world size of about 120x80cm.
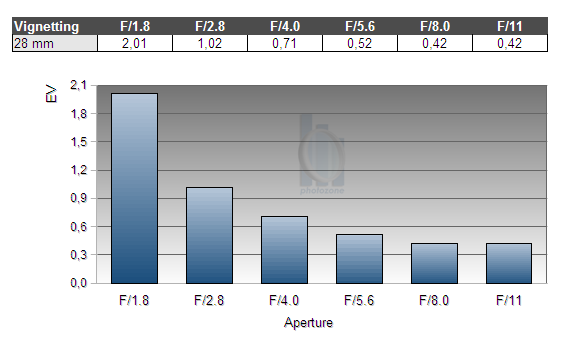
Vignetting
The Sigma lens shows a pronounced amount of light fall-off towards the corners. Wide open, the corners darken a lot. As usual stopping down reduces the issue, but even at rather small apertures there is still almost half a stop of vignetting left.
We're performing our vignetting analysis based on
(uncorrected) JPEGs straight from the camera. The JPG engine of the Nikon D3x features a rather flat
gradation curve, thus has a moderate contrast characteristic, resulting in comparatively low vignetting figures - the
corresponding Canon figures are roughly 40% higher due to the more
aggressive default contrast setting.
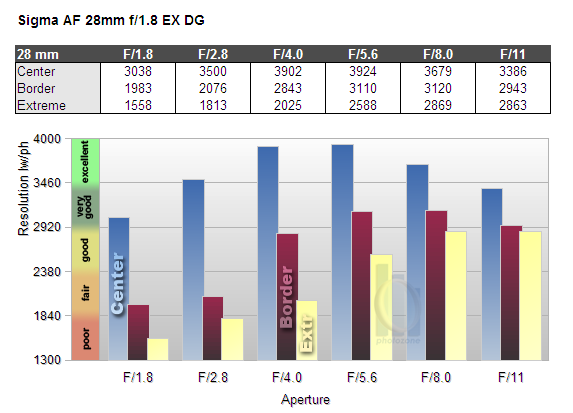
MTF (resolution)
The lens shows very good resolution in the image center wide open, which increases to excellent levels by stopping down.
The borders and corners are a very different story, though. The borders are just fair wide open, but recover to good values at f/4 and very good resolution when stopped down to f/5.6 or f/8. The extreme corners are downright weak wide open and never get beyond good values, even when stopped down considerably.
Please note that the MTF results are not directly comparable across the different systems!
Below is a simplified summary of the formal findings. The chart shows line widths
per picture height (LW/PH) which can be taken as a measure for sharpness.
If you want to know more about the MTF50 figures you may check out the corresponding
Imatest Explanations
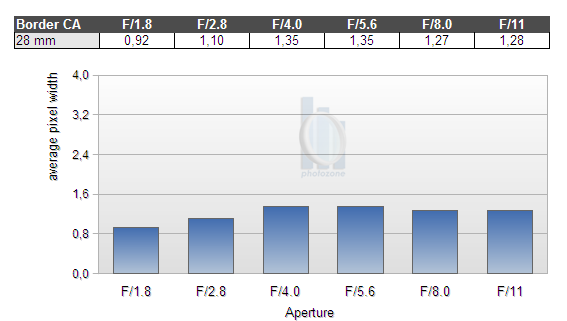
Chromatic Aberrations (CAs)
Chromatic aberrations (color shadows at harsh contrast transitions) are well under control for a wide angle lens and range from just below 1 to 1.35 pixels at the image borders throughout the tested aperture range.
CAs can easily be corrected in software or by the camera itself (most modern Nikon DSLRs remove CAs themselves if you shoot JPGs).
Bokeh
One of the primary usage scenarios for a large aperture lens is to separate the main subject from the background. In such an image the quality of the bokeh (out-of-focus blur) is of major significance.
The Sigma shows quite nervous bokeh both in front of and behind the focal plane at large apertures.
Background highlights also look quite nervous and in addition show pronounced outlining. Towards the image borders, they are cut off at large aperture due to mechanical vignetting.
Both the general bokeh quality as well as background highlights improve in quality by stopping down. However, with a wide angle lens one needs to get quite close to the main subject to still get a significant amount of background blur. The lens' very short MFD comes handy here.

Bokeh Fringing
Bokeh fringing (non-coinciding focal planes of the various colors) are a common issue with relatively fast glass. As you can
notice below the halos have different colors - magenta (red + blue) in front the focus point
and green beyond. Truly "apochromatic" lenses don't show this kind of fringing but these lenses are very rare - especially
below 100mm. Unlike lateral lateral CAs, bokeh fringing cannot easily be fixed in post processing.
Typical for most fast primes, the EX 28 shows some amount of fringing at large aperture settings, which can of course be reduced by stopping down.
|