|
Technology -
Technology
|
If you're on a budget and intend to shop around for a really long tele
lens you may have noticed a quite strange rep of the species - mirror lenses.
For photographic usage there're usually 500mm f/8 mirrors but there're also
faster versions like 500mm f/5.6 and with extreme focal lengths like 1000mm
f/11. Naturally mirror lenses are also widely used for astronomic purposes.
Mirror lenses are comparatively small - e.g. a 500mm f/8 mirror is about
as "big" and light-weight as a mid-range standard zoom. The focal length
is extremely interesting for wildlife photography and the price is usually
hot - very hot. At around 200-400 Euro/$ this is certainly the very cheapest
option in this range. So is it crap or really something worth to be considered
?
In order to impress you here's a shot with a Tokina 500mm f/8 mirror lens:

|
~2m working distance
|
Looks pretty good, doesn't it ? But it tells only part of the story -
the shot above was taken under optimal conditions. More on this later.
Let's have a look at the principal design of a mirror lens first. As the
name implies these lenses are mainly based on mirrors rather than glass elements.
Incoming light gets reflected by a main mirror (located at the back of the
lens) towards a small secondary mirror (at the front) which then reflects
the light back towards the film via a correction (glass) element. The lack
of glass elements (apart from the correction element) is a significant design
advantage compared to classic (refractive) lenses - chromatic aberrations
(visible as color shadows) are virtually absent. Looking at the illustration
below you may notice that the light path gets folded. This is the reason
why these lenses offer such a long focal length while keeping a very small
length. Dependent on the configuration the main mirror can be pretty large
so while quite short most mirrors tend to be rather fat as well. 500/8 mirrors
remain pretty compact but e.g. 500/5.6 or 1000/11 mirrors are about as large
in diameter as the width of an SLR.
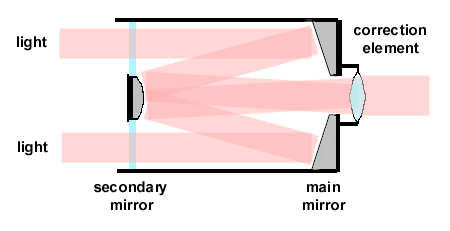
|
schema of a Schmidt-Cassegrain-type mirror lens
|
Unfortunately the design results also in some significant disadvantages
like
- no aperture so it's not possible to control the depth-of-field.
- the mirror reflections eat contrast
- the overall sharpness is usually quite mediocre
- the secondary mirror produces an odd effect donut-like
effect on the out-of-focus high-lights. The following picture illustrates
this problem.

|
working distance ~10m
|
Typically Mirror lenses are quite slow so you may live with the limitation
of a fixed aperture. The contrast performance of a good mirror is roughly
comparable to a typical xx-300 consumer zoom at the long end so that's not
TOO bad (some mirrors are quite unacceptable in this respect though). However,
the unsteady background blur is disturbing indeed and kills the lens for
professional purposes. At first it may be interesting but sooner or later
you recognize that it draws the viewers attention off the main subject.
As mentioned above there're some situations where you can avoid or at least
reduce this donut effect. You've to have a quite even background, an
isolated main object and a close focus distance. The picture at the top
of this document is an example for this. It was taken at a ~2m distance
and avoids any highlighted objects both in the fore- and background thus
resulting in a perfect blur. The picture below looks still pretty
good with a working distance of maybe 5m and a little steeper view towards
the ground - you may already notice some minor hints of donuts here.

|
~5m working distance
|
Conclusion: Yes, mirror lenses produce pictures and under carefully chosen
conditions they may even produce pretty good ones. However, these situations
are rare. For example the shots above were taken in a local bird zoo where
you can get very close to your subject - in real life you'll most likely
end up with situations like in the eagle picture (the 2nd picture) and therefore
with unsteady background blur. Most mirror lenses suffer from a rather
mediocre optical performance. This may all be fine for personal purposes
and for documentation but most likely you'll not be able to sell such pictures.
Therefore a classic (refractive) lens like a 400/5.6 fix-focal or even a
xx-500mm zoom is usually a better solution for a more serious approach. Nonetheless
mirrors are quite cheap and fun to play with.
|